TAPython offers a complete set of menu configuration methods, allowing you to add custom menu items to the UE editor through JSON files
Configurable menu types¶
There are three types of menus, which have the same configuration method but different entry points.
1. Main menu and menus in various editors
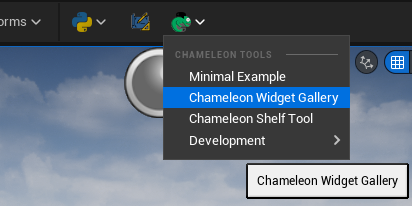
2. Chameleon Tools' Tab Context Menu
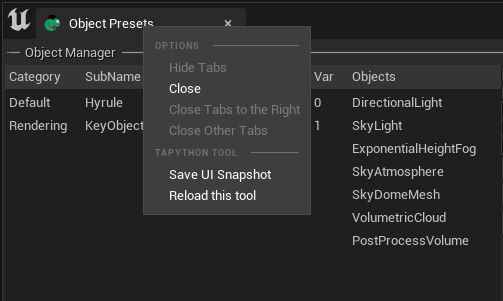
For details, see here: Tab Context Menu, including configuring global common Tab Context Menu and Tab Context Menu for each Chameleon Tool.
3. Slate Widget Context Menu
For example, the following image shows the right-click menu in the SListView widget. Users can operate on the currently selected item in the SListView right-click menu.
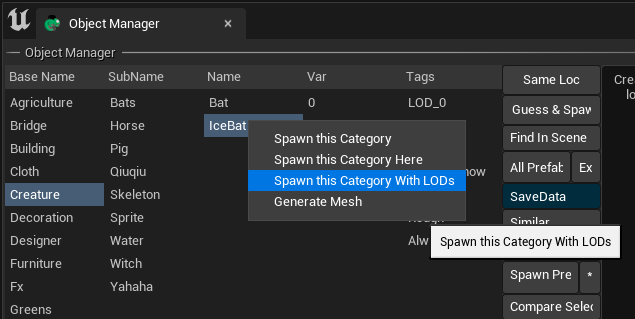
The right-click menu can be added to other Slate components in Chameleon Tools in the same way. For details, see here:Widget Context Menu
Main menu and menus in various editors¶
Most examples can be found here: Built-in Menus, This article only supplements and summarizes.
MenuConfig.json defines all configurable positions
| Menu Item | Details |
|---|---|
| OnMainMenu | Menu entry in the editor's main menu |
| OnToolbar | Main toolbar menu entry, the icon is Python, usually only used for Python tools without a UI |
| OnToolbarChameleon | Chameleon tool icon entry, the icon is a green chameleon, usually used for Chameleon tools with a UI |
| OnOutlineMenu | Context menu in the Outline window |
| OnSelectAssetsMenu | Context menu entry when selecting assets in ContentBrower |
| OnSelectFolderMenu | Right-click menu entry when selecting a directory or clicking on a blank area in ContentBrower |
| OnMaterialEditorMenu | Menu items in the material editor |
| OnPhysicsAssetEditorMenu | Menu items in the Physics Asset editor |
| OnControlRigEditorMenu | Menu items in the ControlRig editor |
Fields in the MenuConfig.json file
| Field Name | Useage | Type |
|---|---|---|
| "items" | Each element is a submenu item, which can be nested into a tree structure | Array |
| "name": | Menu item display name | string |
| "command": | Python code bound to the menu item, supports importing files and calling functions within them | string |
| "ChameleonTools" | The Chameleon Tools to be called is the json file relative path "ChameleonTools": "../Python/Example/MinimalExample.json" |
string |
| "enabled": | Whether to enable the menu item, setting it to false will hide the menu item | bool |
| "canExecuteAction": | Python code, whose return value determines whether the menu item can be clicked. Used to set whether the menu item can be executed based on context (e.g. selecting different assets) | string |
| "tooltip" | Tooltip when the mouse hovers over | string |
| "HasSection" | Whether to add a Python Tools separator named when creating a menu, only | string |
Tool Menu Anchor¶
In addition, we can use the same method to add menu items at all UE preset Tool Menu Anchor locations. For details, see menu_tools_anchor
Configure icons for menu items¶
Using Icons from Style¶
As shown in the image below, we can add icons to Chameleon tools or other menu items. TAPython currently supports two configuration methods:
- Specify a specific FSlateIcon from the Editor style. For example, in the first example below, the icon used is
LevelEditor.Tabs.Detailsfrom the built-in UE editorEditorStyle. - Specify an image path in the Plugin, such as the second example below, which uses the
Resources/flash_32x.pngimage in the TAPython plugin directory.
NOTE
Currently only supports icons in the Plugins\TAPython\Resources directory. These icons need to exist in the directory before the editor starts, otherwise the icons will not be displayed. This is one of the few features in TAPython that does not support dynamic loading
![]()
MenuConfig.json
{
"name": "Some Python Command with Icon",
"command": print('Use EditorStyle Icon'),
"icon": {
"style": "EditorStyle",
"name": "LevelEditor.Tabs.Details"
}
}
{
"name": "Minima lExample",
"ChameleonTools": "../Python/Example/MinimalExample.json",
"icon": {
"ImagePathInPlugin": "Resources/flash_32x.png"
}
},
{
"name": "Chameleon Shelf Tool",
"ChameleonTools": "../Python/ShelfTools/Shelf.json",
"icon": {
"style": "ChameleonStyle",
"name": "Resources.briefcase_32x_png"
}
},
In the last example above, we used ChameleonStyle. It is an automatically generated EditorStyle. The rule is that any image (.png, .svg) stored in the Plugins\TAPython\Resources directory, except for the SlateIcon registered in the plugin's C++ code, will be automatically registered in ChameleonStyle. Therefore, the third example is equivalent to the following code:
{
"name": "Minima lExample",
"ChameleonTools": "../Python/Example/MinimalExample.json",
"icon": {
"ImagePathInPlugin": "Resources/briefcase_32x.png"
}
},
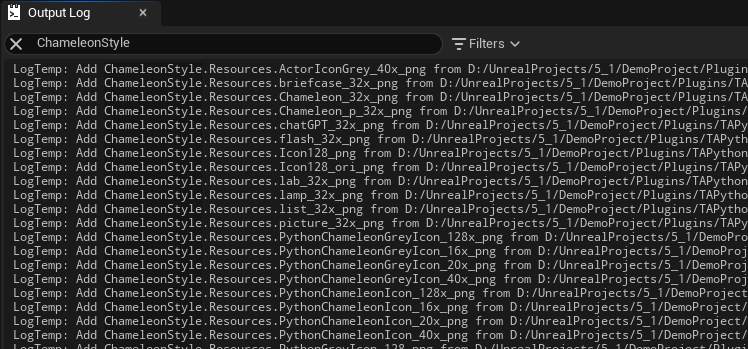
To see which icons are available in ChameleonStyle, you can find the following output in the OutputLog after the editor is opened. Developers can also add their own icons to the Resource directory as needed.
TIP
Currently supports .png and .svg (UE5) image formats.
Extra
Requiring icons to be placed in the plugin's Resources directory can be inconvenient for users. In the future, we will add functionality to directly load images as icons dynamically.
More menu item technical details